Montessori pedagogy
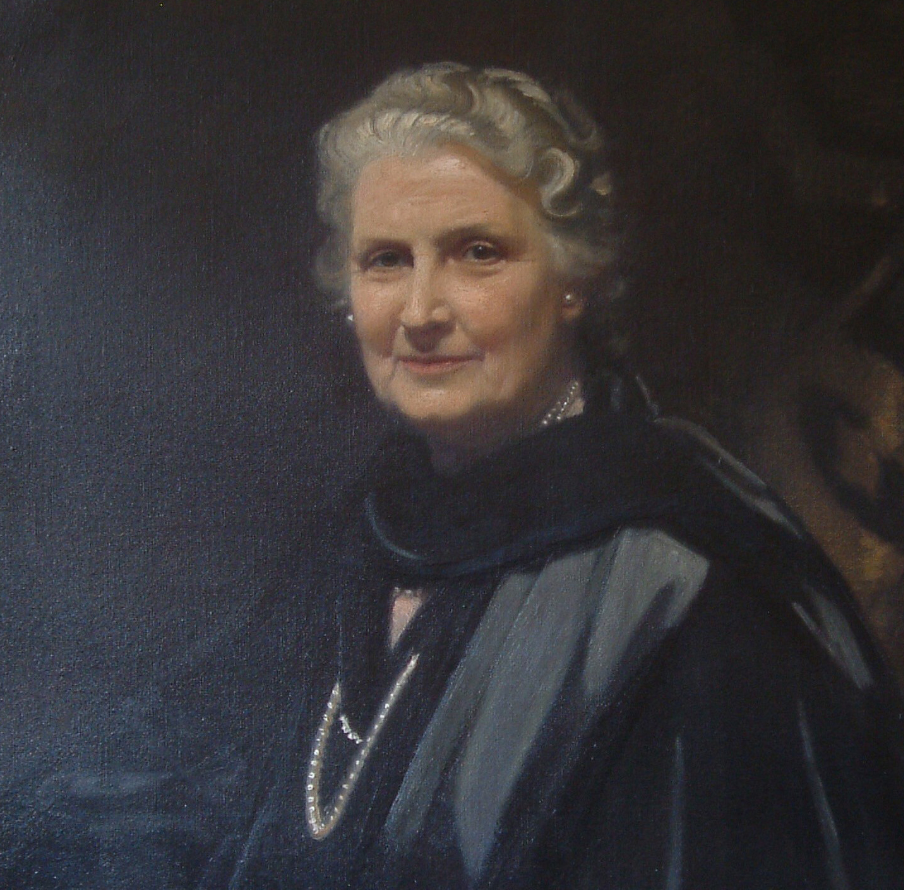

Maria Montessori (1870-1952)
The first woman doctor in Italy, Maria Montessori was an educational pioneer renowned for her innovative approach centred on children's autonomy. She developed a teaching method based on scientific observation of children's cognitive and psychological development.
Maria Montessori revolutionised education by encouraging learning through experience and the use of teaching materials. Her legacy lives on in the pedagogy that bears her name and has had an impact on education worldwide.
Pedagogy
At the Maria Montessori International School, pupils are taught in a bilingual Montessori environment, comprising a pre-school section (3-4 years) and a primary section (4-6 years), with a French-speaking teacher and an English-speaking teacher.
Teaching is provided in French and English according to the Montessori programme and follows the Plan d'Etudes Romand (PER) of the Swiss public primary school system (Harmos 1-2P), from the age of four.
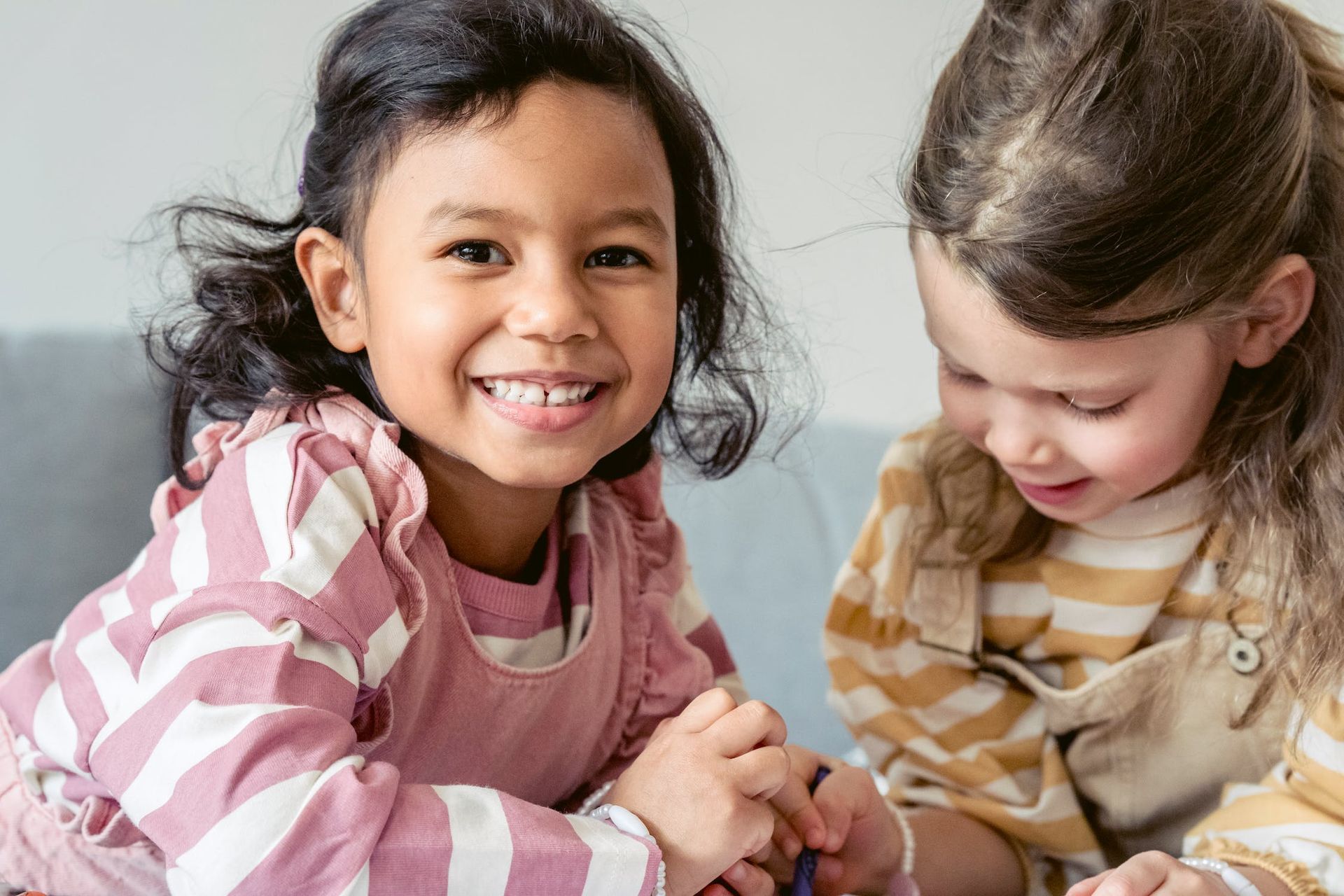
A mix of ages
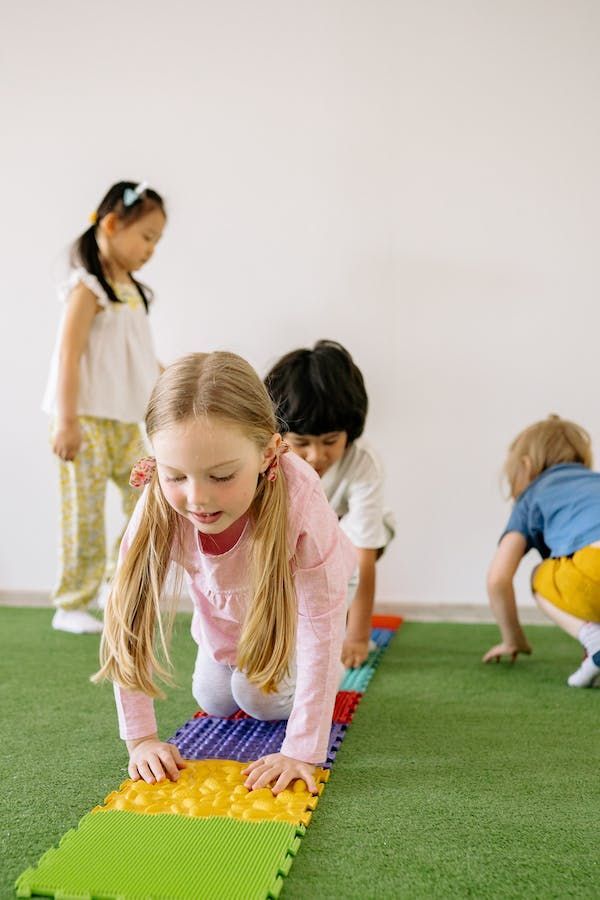
The children are taught in a mixed-age class, from 3 to 6 years old. They follow the same natural laws of development, in accordance with the first development plan of the Montessori pedagogy.
The children go through sensitive periods, such as those of language, order, coordination of movements, sensory refinement, social development and small objects. During these periods, they develop a heightened sensitivity to a particular area that guides them in their quest for autonomy.
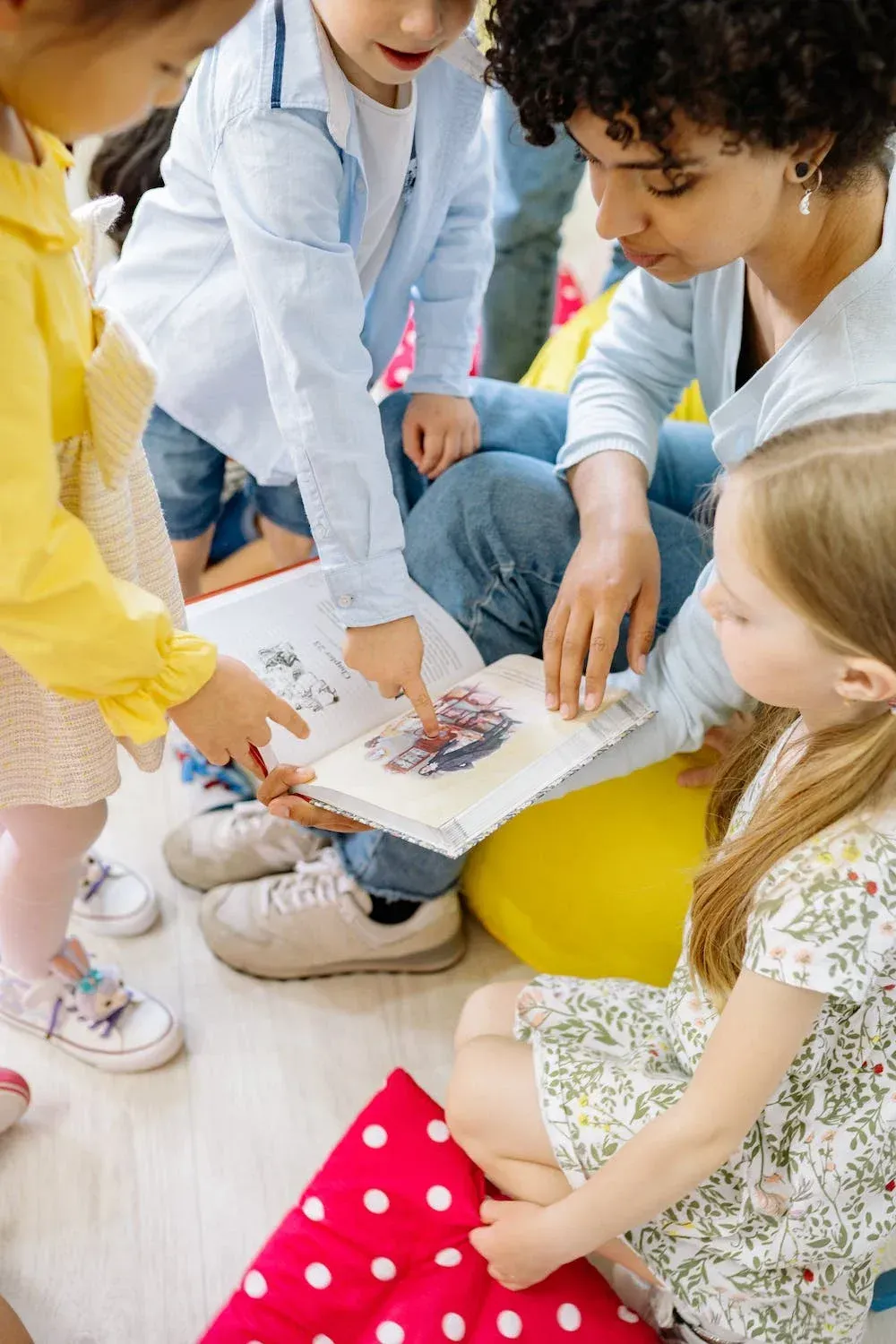
Observation and respect for individual rhythm are essential. Children learn to live in a community and interact with children of different ages. They develop their social skills and learn to work in pairs. The younger children observe and draw inspiration from the older ones, while the older ones take on the role of mentors and role models, guiding, helping and collaborating with the younger ones.
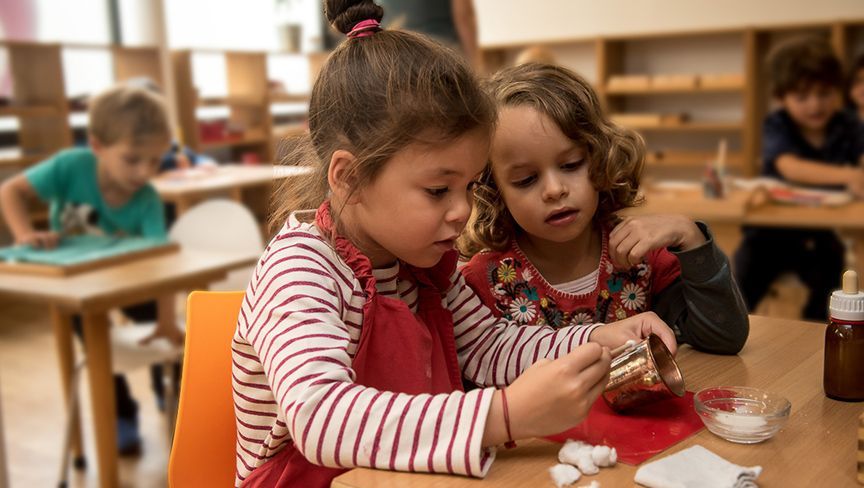
A prepared environment
Children work in an environment specially prepared to meet their developmental needs: the furniture and equipment are adapted to their size and strength. Children have the freedom to move around freely and choose the materials they wish to work with.
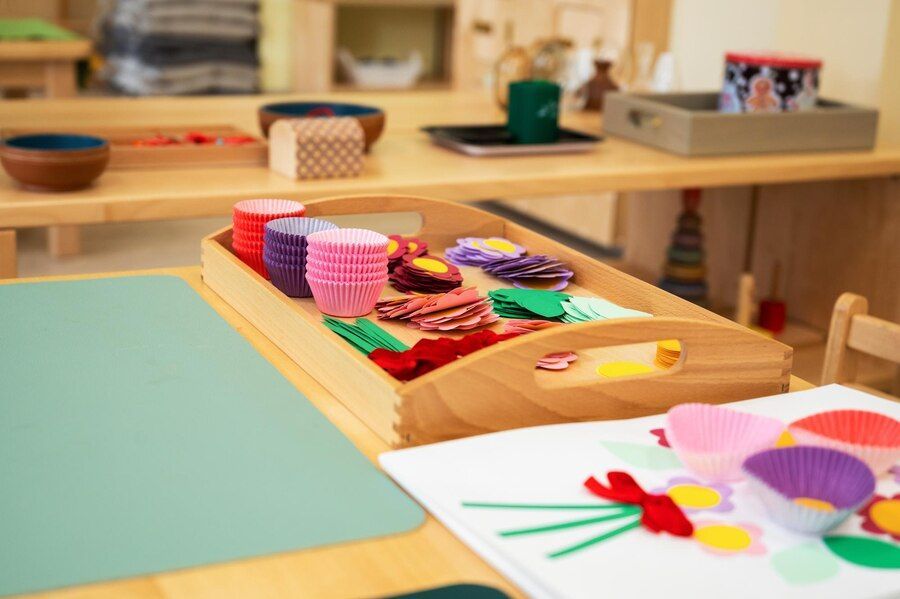
Each learning area is equipped with the appropriate Montessori materials, offering orderly, structured activities that nurture children's absorbing minds. All materials encourage self-directed learning and exploration, allowing children to develop their intelligence independently.
The prepared educator
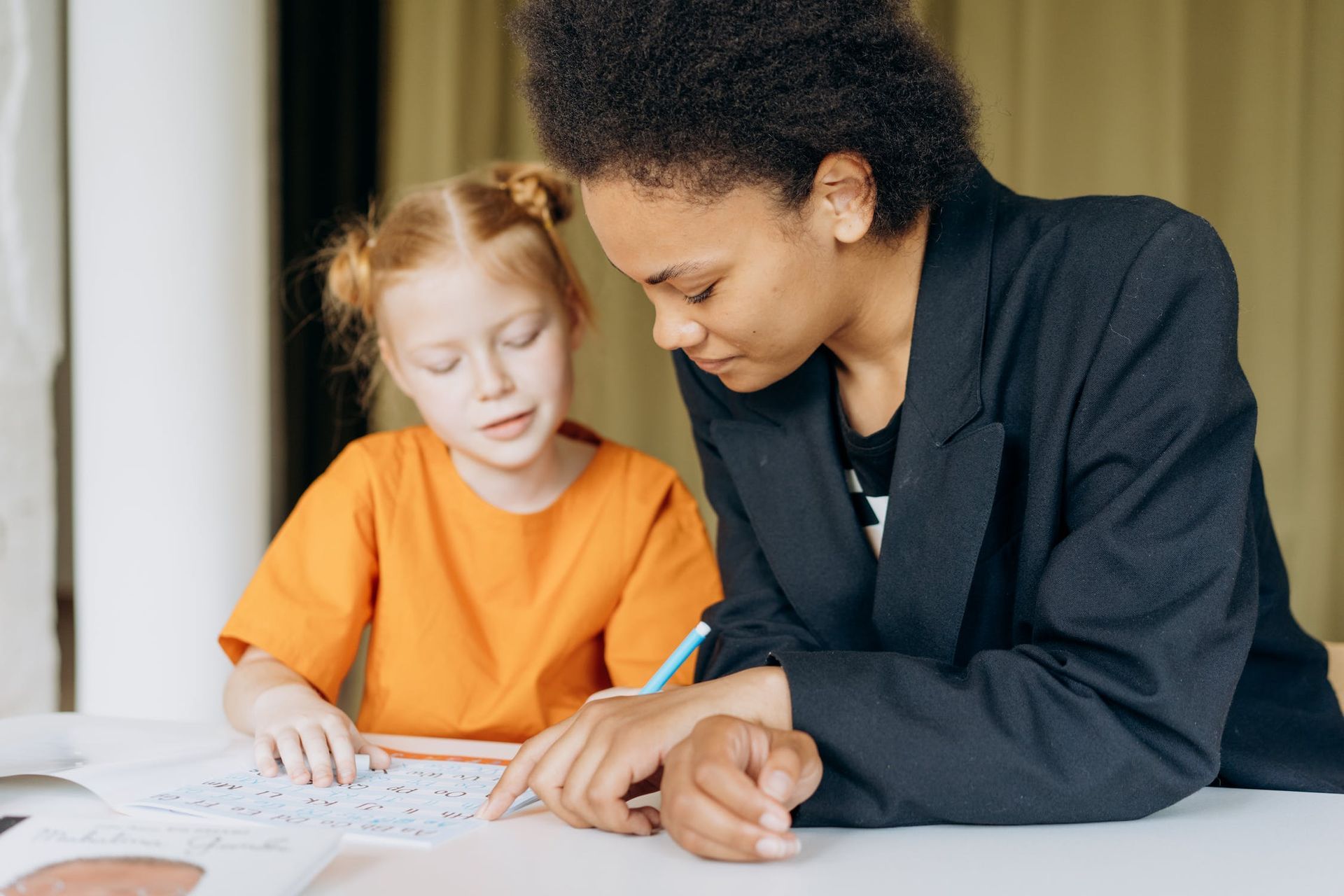
The role of the educator is to act as a guide and facilitate the link between the educational material and the child.
Through morning work cycles of at least two and a half hours, the educator encourages continuous independent activity in the child and guides him/her through the five areas, helping him/her to direct his/her attention towards specific activities.
So it's not the teacher who helps the child to develop, it's the activities that encourage the development of attention, movement and repetition, all of which are necessary to cultivate concentration.
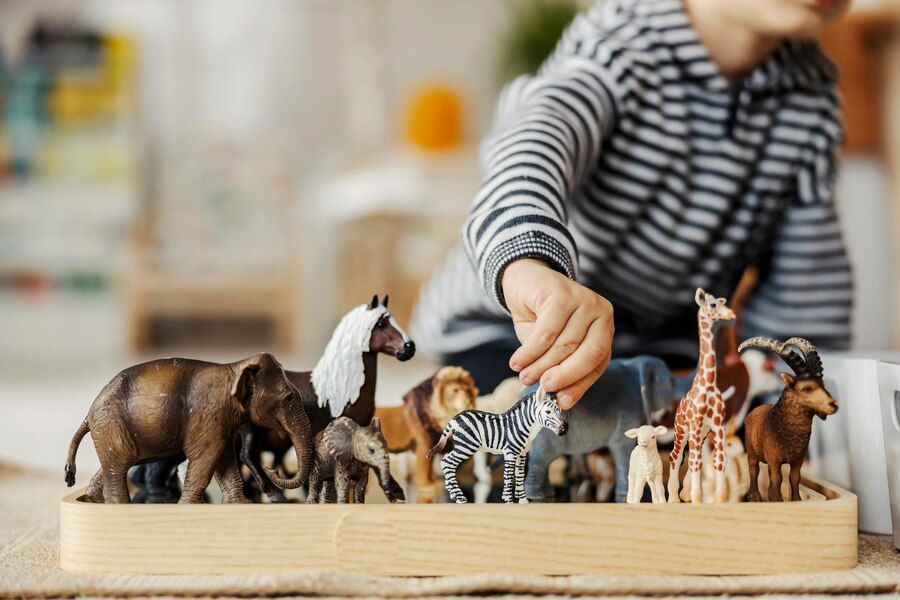
Mastering fundamental concepts
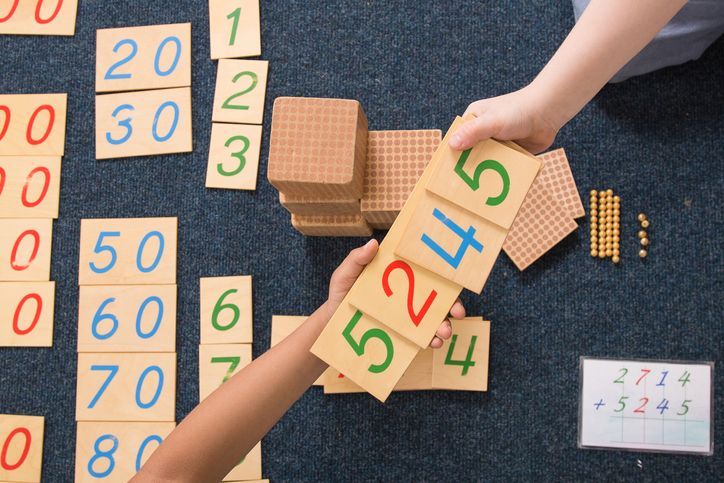
Pupils work daily using the teaching and scientific materials developed by Maria Montessori, in the learning areas of practical life, the senses, language, mathematics and culture (geography, zoology, botany, music, art) to acquire fundamental concepts.
Montessori Sports and swimming lessons
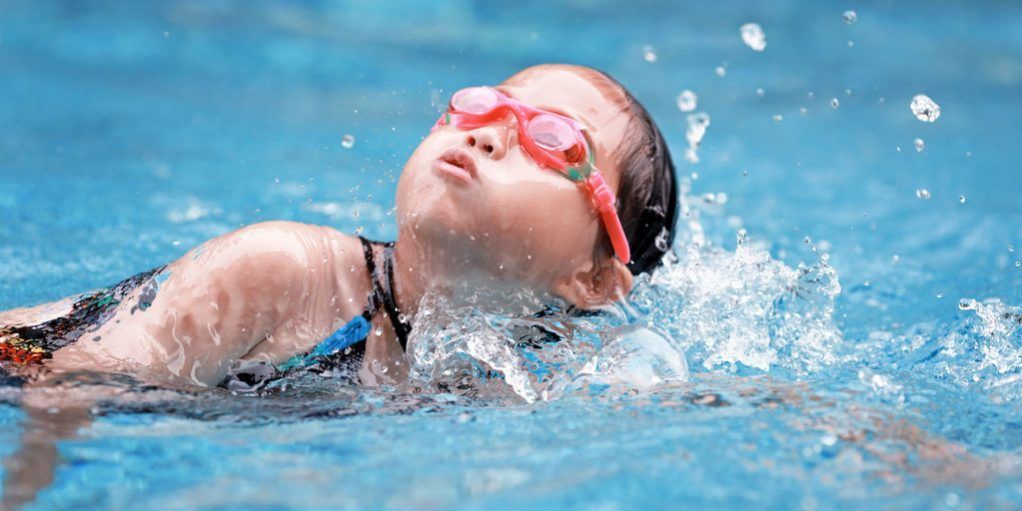
Sports activities are an integral part of the Montessori programme. Pupils practise motor coordination exercises in accordance with the Montessori Sports programme. The International Maria Montessori School offers swimming lessons at the Varembé swimming pool, provided by the ENG (Ecole de Natation de Genève).
« Schools must become places where children can live in freedom. »
Maria Montessori
Cultural and educational activities
Cultural outings: Pupils take part in cultural outings (theatre, dance, music, etc.) in line with the AGEP (Association Genevoise des Ecoles Privées) annual programme.
Educational outings: Each year, two educational outings are offered to the pupils, one in autumn and one in spring.
Nature outings: Pupils at the school benefit from nature education through organised or spontaneous outings. Inspired by the Forest Schools concept, we will be organising educational days in the forest.
Educating for peace
Access
TPG, bus line 5 or 8, "Intercontinental" stop - Parking: Chemin du Petit-Saconnex
Opening hours
Monday, Tuesday, Thursday and Friday
from 08:30 to 17:30
Wednesday
from 08:30 to 11:45
Navigation